Cracking the Beta Code: A Voyage through Market Sensitivity
Welcome, fellow adventurers, to the financial journey of a lifetime, where numbers transform into sailing ships navigating the vast sea of stocks. Today, our compass points us toward Beta, a metric that acts as the ship's anchor, helping us gauge the tempests and calms of the market waves. Join us as we embark on this expedition to understand Beta, its definition, calculation, significance, and how it steers the course of our investment vessel.
Defining Beta: The Navigator's Compass
Beta, in the language of finance, is a measure of a stock or investment's sensitivity to market movements. It's like the compass that tells sailors how their ship will respond to the ebb and flow of the market tides. A Beta of 1 indicates that the investment moves in line with the market, while a Beta less than 1 suggests lower volatility, and a Beta greater than 1 implies higher volatility.
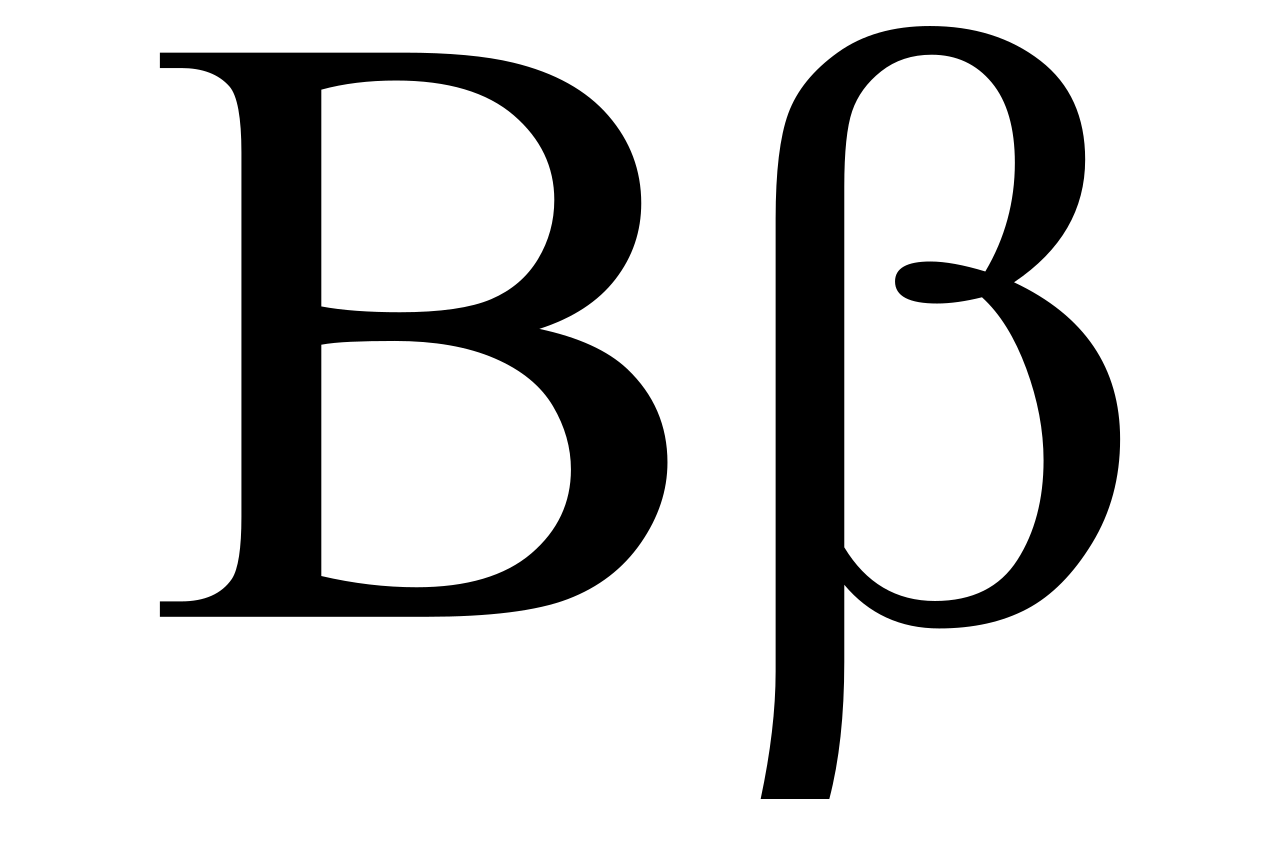 |
| Cracking the Beta Code: A Voyage through Market Sensitivity |
The Formula: Unveiling the Navigation Chart
Beta=Covariance between the stock’s returns and market returnsVariance of the market returnsBeta=Variance of the market returnsCovariance between the stock’s returns and market returns
Let's demystify this equation:
- Covariance: A statistical measure that indicates the degree to which two variables move together. In Beta's case, it's the movement of the stock's returns in relation to the market returns.
- Variance: A measure of the dispersion of a set of values. In Beta's equation, it quantifies the variability of the market returns.
Interpreting Beta: Navigating the Market Waves
- Beta = 1: A Beta of 1 suggests that the stock tends to move in sync with the market. It's like sailing a ship that floats along with the rhythm of the ocean waves. If the market rises, the stock rises; if the market falls, the stock falls.
- Beta < 1: A Beta less than 1 indicates that the stock is less volatile than the market. Picture it as a ship with a steady course, gliding through the waters with less turbulence than the surrounding waves. In calmer seas, it may not rise as high, but in storms, it won't sink as low.
- Beta > 1: Conversely, a Beta greater than 1 signals that the stock is more volatile than the market. This ship is a bit of an adventurer, riding the market waves with heightened enthusiasm. In surges, it climbs higher, and in downturns, it may plunge further.
The Significance of Beta: Navigating Investment Strategies
Risk Assessment:
- Beta is a crucial tool for assessing the risk associated with a particular investment. A Beta less than 1 indicates lower risk, while a Beta greater than 1 suggests higher risk. It's the lighthouse that warns sailors of potential rocky shores.
Portfolio Diversification:
- For the wise captain managing a fleet of investments, Beta helps in diversification. Balancing investments with different Beta values can create a portfolio that weathers market storms with resilience.
Investment Strategy Alignment:
- Investors with varying risk appetites can use Beta to align their investment strategies. Conservative investors may opt for low Beta stocks, while those seeking adventure might set sail with high Beta stocks.
Market Timing:
- Beta aids in market timing decisions. During bullish periods, high Beta stocks may offer greater returns, while low Beta stocks might provide stability during market downturns. It's the tide chart guiding sailors on when to set sail.
Performance Evaluation:
- Beta is not only a tool for risk assessment but also for evaluating past performance. Understanding how a stock has historically responded to market movements helps investors anticipate future behavior. It's the logbook recording the ship's journey through past seas.
Challenges in Beta Navigation: Plotting the Uncharted Waters
- Sensitivity to Market Conditions:
- Beta is sensitive to the time period considered for its calculation. Short-term Beta may not reflect the long-term market sensitivity of a stock accurately.
- Limited Predictive Power:
- Beta is a historical measure and may not perfectly predict future market behavior. Market dynamics can change, and unforeseen events may alter a stock's sensitivity.
- Industry and Company-Specific Factors:
- Beta considers the overall market but may overlook industry or company-specific factors influencing a stock's performance.
- Marketwide Shocks:
- In times of extreme marketwide shocks, Beta may not capture the full extent of a stock's deviation from its historical behavior.
Charting a Course with Beta: The Navigator's Tale
As we navigate the seas of the stock market, Beta emerges as the trusted navigator, helping us steer clear of rocky shoals and find the wind in our investment sails. Understanding the significance of Beta allows us to embark on well-informed journeys, choosing investments that align with our risk preferences and market expectations. So, fellow adventurers, set your sails, consult your Beta charts, and may your investments sail through calm waters and weather market storms with resilience. Bon voyage!